HIF stabilizers in the management of renal anemia: from bench to bedside to pediatrics
- PMID: 29569190
- PMCID: PMC6349802
- DOI: 10.1007/s00467-017-3849-3
HIF stabilizers in the management of renal anemia: from bench to bedside to pediatrics
Abstract
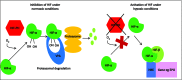
Anemia is a common complication of chronic kidney disease (CKD) in adult and pediatric patients. It has traditionally been treated with erythropoietin therapy and iron supplementation, with great success. With the discovery of the major transcription factor hypoxia inducible factor (HIF) for the erythropoietin gene in 1992, molecules were created that inhibit the HIF prolyl-hydroxylase enzyme. This new class of drug-called HIF stabilizers, or HIF prolyl-hydroxylase inhibitors-prevents the proteasomal degradation of HIF-α, thereby inducing upregulation of the erythropoietin gene. This new strategy for treating CKD anemia is already in phase III clinical trials in adults, and the potential advantages of this therapy are that it is orally active (thereby avoiding injections), and patients are exposed to lower circulating levels of erythropoietin. The long-term safety of this strategy, however, requires elucidation in these trials, particularly since there are many other hypoxia-sensitive genes, notably, angiogenic factors such as vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGF), as well as glycolytic enzymes. As with all new therapies, it is only once a positive benefit: risk profile has been ascertained in adults that the treatment will translate across into pediatrics. Specific issues in the pediatric CKD population are discussed in this review.
Keywords: Anemia; Chronic kidney disease; HIF prolyl-hydroxylase inhibitor; HIF stabilizer.
Conflict of interest statement
Iain Macdougall has received consultancy fees, speaker fees, and research support from a number of manufacturers of HIF stabilizers, including FibroGen, Astellas, GlaxoSmithKline, Akebia, and Bayer. Dalvir Kular reports no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Renal anemia and hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor].Rinsho Ketsueki. 2021;62(5):371-377. doi: 10.11406/rinketsu.62.371. Rinsho Ketsueki. 2021. PMID: 34108317 Japanese.
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor in the treatment of anemia in chronic kidney disease.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2020 Jul;29(4):414-422. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000617. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2020. PMID: 32452915 Review.
-
JTZ-951 (enarodustat), a hypoxia-inducibe factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor, stabilizes HIF-α protein and induces erythropoiesis without effects on the function of vascular endothelial growth factor.Eur J Pharmacol. 2019 Sep 15;859:172532. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172532. Epub 2019 Jul 10. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31301309
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors for renal anemia in chronic kidney disease: Advantages and disadvantages.Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Dec 5;912:174583. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174583. Epub 2021 Oct 19. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34678238 Review.
-
Investigational hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors (HIF-PHI) for the treatment of anemia associated with chronic kidney disease.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2018 Jul;27(7):613-621. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2018.1493455. Epub 2018 Jul 12. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29975110 Review.
Cited by
-
Kidney disease trials for the 21st century: innovations in design and conduct.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020 Mar;16(3):173-185. doi: 10.1038/s41581-019-0212-x. Epub 2019 Oct 31. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 31673162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anemia of Inflammation with An Emphasis on Chronic Kidney Disease.Nutrients. 2019 Oct 11;11(10):2424. doi: 10.3390/nu11102424. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31614529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alternative splicing of CEACAM1 by hypoxia-inducible factor-1α enhances tolerance to hepatic ischemia in mice and humans.Sci Transl Med. 2023 Aug 2;15(707):eadf2059. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.adf2059. Epub 2023 Aug 2. Sci Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37531413 Free PMC article.
-
Current Status of Renal Anemia Pharmacotherapy-What Can We Offer Today.J Clin Med. 2021 Sep 15;10(18):4149. doi: 10.3390/jcm10184149. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34575261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Erythropoietin-Stimulating Agent Hyporesponsiveness in Patients Living with Chronic Kidney Disease.Kidney Dis (Basel). 2022 Jan 14;8(2):103-114. doi: 10.1159/000521162. eCollection 2022 Mar. Kidney Dis (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35527989 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hooper SR, Gerson AC, Johnson RJ, Mendley SR, Shinnar S, Lande MB, Matheson MB, Gipson DS, Morgenstern B, Warady BA, Furth SL. Neurocognitive, social-behavioral, and adaptive functioning in preschool children with mild to moderate kidney disease. J Dev Behav Pediatr. 2016;37:231–238. doi: 10.1097/DBP.0000000000000267. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials