Ab-interno trabeculotomy-related glaucoma surgeries
- PMID: 31198665
- PMCID: PMC6557068
- DOI: 10.4103/tjo.tjo_38_19
Ab-interno trabeculotomy-related glaucoma surgeries
Abstract
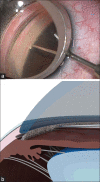
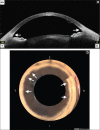
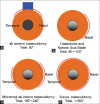
Reductions of intraocular pressure during trabeculotomy result from relieving the resistance to aqueous flow by cleavage of the trabecular meshwork and inner walls of Schlemm's canal at the point of outflow resistance of the aqueous humor. Since trabeculotomy does not result in bleb formation, development of late-onset sight-threatening complications, such as hypotony maculopathy and endophthalmitis, that are associated occasionally with trabeculectomy develop less frequently after trabeculotomy. The ab-interno approach is used in several new procedures, including the Trabectome, Kahook Dual Blade, microhook abinterno trabeculotomy, and 360° suture trabeculotomy, instead of the ab-externo approach as in conventional trabeculotomy. These newly developed novel, minimally invasive, and trabeculotomy-related glaucoma surgeries can be good options for certain glaucoma cases, including early-stage open-angle glaucoma, developmental glaucoma, and glaucoma in elderly patients.
Keywords: Ab-externo trabeculotomy; Kahook Dual Blade; Trabectome; microhook ab-interno trabeculotomy; minimally invasive glaucoma surgery; suture ab-interno trabeculotomy.
Conflict of interest statement
The microhooks used were codeveloped by Masaki Tanito, MD, PhD, and Inami and Co., Ltd. (Tokyo, Japan) and provided by Inami and Co., Ltd. Dr. Tanito receives royalties from Inami and Co., Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ab interno Schlemm's Canal Surgery.Dev Ophthalmol. 2017;59:127-146. doi: 10.1159/000458492. Epub 2017 Apr 25. Dev Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28442693 Review.
-
Circumferential Schlemm's Canal Surgery in Adult and Pediatric Glaucoma.Curr Eye Res. 2019 Dec;44(12):1281-1290. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2019.1659975. Epub 2019 Aug 29. Curr Eye Res. 2019. PMID: 31438743 Review.
-
Minimally Invasive Glaucoma Surgery.2023 Aug 25. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2023 Aug 25. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 35881761 Free Books & Documents.
-
Microhook ab interno trabeculotomy, a novel minimally invasive glaucoma surgery.Clin Ophthalmol. 2017 Dec 20;12:43-48. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S152406. eCollection 2018. Clin Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 29339920 Free PMC article.
-
Ab interno trabecular bypass surgery with Trabectome for open-angle glaucoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Feb 4;2(2):CD011693. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011693.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33580495 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
36-Month Outcomes of Standalone Kahook Dual Blade Goniotomy Compared with Ab-Interno Closed Conjunctiva Xen Gel Stent Implantation.Clin Ophthalmol. 2024 Sep 16;18:2593-2603. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S473303. eCollection 2024. Clin Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39309685 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of 1-year effectiveness between phaco-microhook ab-interno trabeculotomy and phaco-iStent trabecular micro-bypass stent in primary open-angle glaucoma with low-teen intraocular pressure.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2024 Aug 19. doi: 10.1007/s00417-024-06607-6. Online ahead of print. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39160440
-
Are Prophylactic Systemic Antibiotics Required in Patients with Cataract Surgery at Local Anesthesia?Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Nov 27;19(23):15796. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192315796. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36497871 Free PMC article.
-
Proportion of Glaucoma Types and Surgeries Among Young, Pre-Old, Old, and Oldest-Old Age Groups or Different Sex Groups.Clin Ophthalmol. 2022 Jun 7;16:1815-1819. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S370082. eCollection 2022. Clin Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35698600 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Peripheral Anterior Synechiae Formation After Microhook Ab-interno Trabeculotomy Using a 360-Degree Gonio-Camera.Clin Ophthalmol. 2021 Apr 19;15:1629-1638. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S306834. eCollection 2021. Clin Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 33907377 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chihara E, Nishida A, Kodo M, Yoshimura N, Matsumura M, Yamamoto M, et al. Trabeculotomy ab externo: An alternative treatment in adult patients with primary open-angle glaucoma. Ophthalmic Surg. 1993;24:735–9. - PubMed
-
- Tanihara H, Negi A, Akimoto M, Terauchi H, Okudaira A, Kozaki J, et al. Surgical effects of trabeculotomy ab externo on adult eyes with primary open angle glaucoma and pseudoexfoliation syndrome. Arch Ophthalmol. 1993;111:1653–61. - PubMed
-
- Tanito M, Ohira A, Chihara E. Surgical outcome of combined trabeculotomy and cataract surgery. J Glaucoma. 2001;10:302–8. - PubMed
-
- Tanito M, Ohira A, Chihara E. Factors leading to reduced intraocular pressure after combined trabeculotomy and cataract surgery. J Glaucoma. 2002;11:3–9. - PubMed
-
- Minckler DS, Baerveldt G, Alfaro MR, Francis BA. Clinical results with the trabectome for treatment of open-angle glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 2005;112:962–7. - PubMed

