Phytochemical Composition, Bioactive Compounds, and Antioxidant Properties of Different Parts of Andrographis macrobotrys Nees
- PMID: 37240810
- PMCID: PMC10223075
- DOI: 10.3390/life13051166
Phytochemical Composition, Bioactive Compounds, and Antioxidant Properties of Different Parts of Andrographis macrobotrys Nees
Abstract
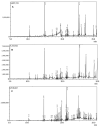
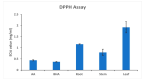
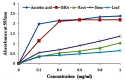
Andrographis macrobotrys Nees is an ethnomedicinal plant belonging to the family Acanthaceae, distributed in the moist deciduous and semi-evergreen forests of the southern Western Ghats of India. The objective of this research was to determine the phytochemical composition and bioactive chemical components using gas chromatography and mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and to check the antioxidant potential of the plant part extracts. A. macrobotrys roots, stems, and leaves were obtained from the species' natural habitat in the Western Ghats, India. The bioactive compounds were extracted using a Soxhlet extractor at 55-60 °C for 8 h in methanol. Identification analysis of A. macrobotrys bioactive compound was performed using GC-MS. Quantitative estimation of phytochemicals was carried out, and the antioxidant capacity of the plant extracts was determined by 2,2'-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radical scavenging (DPPH) and ferric reducing assays (FRAP). A. macrobotrys has a higher concentration of phenolics in its stem extract than in its root or leaf extracts (124.28 mg and 73.01 mg, respectively), according to spectrophotometric measurements. GC-MS analysis revealed the presence of phytochemicals such as azulene, 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol, benzoic acid, 4-ethoxy-ethyl ester, eicosane, 3-heptadecanol, isopropyl myristate, hexadecanoic acid methyl ester, hexadecanoic acid, 1-butyl-cyclohexanol, 9,12-octadecadienoic acid, alpha-monostearin, and 5-hydroxy-7,8-dimethoxyflavone belonging to various classes of flavonoids, terpenoids, phenolics, fatty acids, and aromatic compounds. Significant bioactive phytochemicals include 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol, 2-methoxy-4-vinylphenol, 5-hydroxy-7,8-dimethoxyflavone, azulene, salvigenin, squalene, and tetrapentacontane. In addition, the antioxidant capability of each of the three extracts was assessed. The stem extract demonstrated impressive DPPH scavenging and ferric reduction activities, with EC50 values of 79 mg/mL and 0.537 ± 0.02 OD at 0.2 mg/mL, respectively. The results demonstrated the importance of A. macrobotrys as a source of medicine and antioxidants.
Keywords: Andrographis; GS-MS analysis; antioxidants; bioactive compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative Assessment of Phytoconstituents, Antioxidant Activity and Chemical Analysis of Different Parts of Milk Thistle Silybum marianum L.Molecules. 2022 Apr 20;27(9):2641. doi: 10.3390/molecules27092641. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35565993 Free PMC article.
-
Solvent Extraction and Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Annona squamosa L. Seeds for Determination of Bioactives, Fatty Acid/Fatty Oil Composition, and Antioxidant Activity.J Diet Suppl. 2018 Sep 3;15(5):613-623. doi: 10.1080/19390211.2017.1366388. Epub 2017 Nov 2. J Diet Suppl. 2018. PMID: 29095663
-
Antioxidant activities and phytochemical constituents of Antidesma thwaitesianum Müll. Arg. leaf extracts.J Integr Med. 2017 Jul;15(4):310-319. doi: 10.1016/S2095-4964(17)60334-0. J Integr Med. 2017. PMID: 28659236
-
Phytochemical Analysis, GC-MS Identification of Bioactive Compounds, and In Vitro Antioxidant Activities of Resin of Garcinia indica (Thouars) Choisy.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2023 Jul;195(7):4570-4582. doi: 10.1007/s12010-023-04343-x. Epub 2023 Jan 27. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36705843
-
Angolan Cymbopogon citratus used for therapeutic benefits: nutritional composition and influence of solvents in phytochemicals content and antioxidant activity of leaf extracts.Food Chem Toxicol. 2013 Oct;60:413-8. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2013.07.064. Epub 2013 Aug 1. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23911554
Cited by
-
Harnessing the Power of Plants: A Green Factory for Bioactive Compounds.Life (Basel). 2023 Oct 11;13(10):2041. doi: 10.3390/life13102041. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895423 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional Value, Fatty Acid and Phytochemical Composition, and Antioxidant Properties of Mysore Fig (Ficus drupacea Thunb.) Fruits.Foods. 2024 Sep 7;13(17):2845. doi: 10.3390/foods13172845. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39272612 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sen S., Chakraborty R., De B. Challenges and opportunities in the advancement of herbal medicine: India’s position and role in a global context. J. Herb. Med. 2011;1:67–75. doi: 10.1016/j.hermed.2011.11.001. - DOI
-
- Subramanian R., Zaini Asmawi M., Sadikun A. A Bitter plant with a sweet future? A comprehensive review of an oriental medicinal plant: Andrographis paniculata. Phytochem. Rev. 2012;11:39–75. doi: 10.1007/s11101-011-9219-z. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous